fftn(a, s=None, axes=None, norm=None)
This function computes the N-dimensional discrete Fourier Transform over any number of axes in an M-dimensional array by means of the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT).
The output, analogously to fft
, contains the term for zero frequency in the low-order corner of all axes, the positive frequency terms in the first half of all axes, the term for the Nyquist frequency in the middle of all axes and the negative frequency terms in the second half of all axes, in order of decreasingly negative frequency.
See numpy.fft
for details, definitions and conventions used.
Input array, can be complex.
Shape (length of each transformed axis) of the output ( s[0]
refers to axis 0, s[1]
to axis 1, etc.). This corresponds to n
for fft(x, n)
. Along any axis, if the given shape is smaller than that of the input, the input is cropped. If it is larger, the input is padded with zeros. if s is not given, the shape of the input along the axes specified by :None:None:`axes` is used.
Axes over which to compute the FFT. If not given, the last len(s)
axes are used, or all axes if s is also not specified. Repeated indices in :None:None:`axes` means that the transform over that axis is performed multiple times.
Normalization mode (see numpy.fft
). Default is "backward". Indicates which direction of the forward/backward pair of transforms is scaled and with what normalization factor.
The "backward", "forward" values were added.
If s and :None:None:`axes` have different length.
If an element of :None:None:`axes` is larger than than the number of axes of a.
The truncated or zero-padded input, transformed along the axes indicated by :None:None:`axes`, or by a combination of s and a, as explained in the parameters section above.
Compute the N-dimensional discrete Fourier Transform.
fft
The one-dimensional FFT, with definitions and conventions used.
fft2
The two-dimensional FFT.
fftshift
Shifts zero-frequency terms to centre of array
ifftn
The inverse of :None:None:`fftn`, the inverse n-dimensional FFT.
numpy.fft
Overall view of discrete Fourier transforms, with definitions and conventions used.
rfftn
The n-dimensional FFT of real input.
>>> a = np.mgrid[:3, :3, :3][0]
... np.fft.fftn(a, axes=(1, 2)) array([[[ 0.+0.j, 0.+0.j, 0.+0.j], # may vary [ 0.+0.j, 0.+0.j, 0.+0.j], [ 0.+0.j, 0.+0.j, 0.+0.j]], [[ 9.+0.j, 0.+0.j, 0.+0.j], [ 0.+0.j, 0.+0.j, 0.+0.j], [ 0.+0.j, 0.+0.j, 0.+0.j]], [[18.+0.j, 0.+0.j, 0.+0.j], [ 0.+0.j, 0.+0.j, 0.+0.j], [ 0.+0.j, 0.+0.j, 0.+0.j]]])
>>> np.fft.fftn(a, (2, 2), axes=(0, 1)) array([[[ 2.+0.j, 2.+0.j, 2.+0.j], # may vary [ 0.+0.j, 0.+0.j, 0.+0.j]], [[-2.+0.j, -2.+0.j, -2.+0.j], [ 0.+0.j, 0.+0.j, 0.+0.j]]])
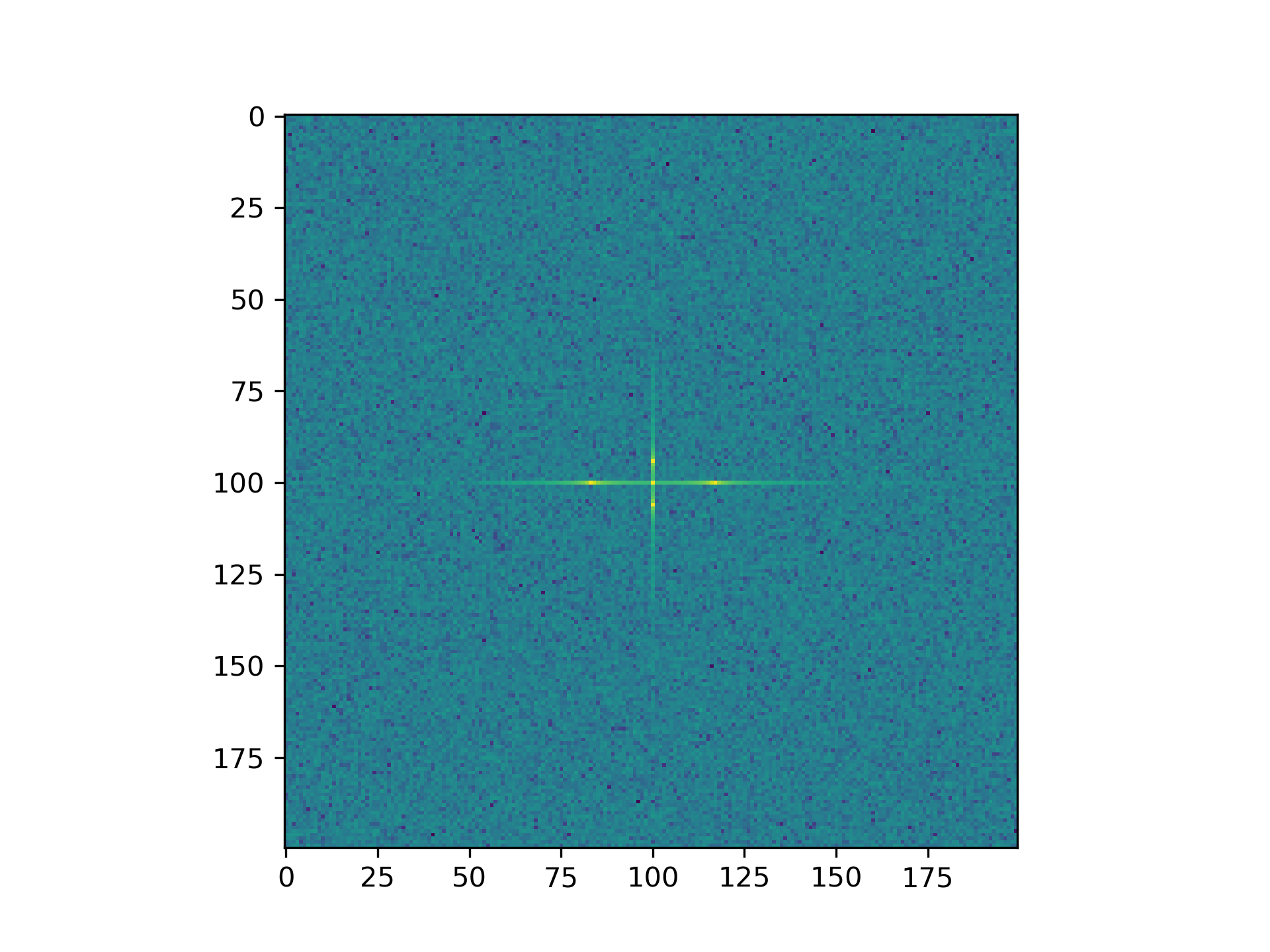
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
... [X, Y] = np.meshgrid(2 * np.pi * np.arange(200) / 12,
... 2 * np.pi * np.arange(200) / 34)
... S = np.sin(X) + np.cos(Y) + np.random.uniform(0, 1, X.shape)
... FS = np.fft.fftn(S)
... plt.imshow(np.log(np.abs(np.fft.fftshift(FS))**2)) <matplotlib.image.AxesImage object at 0x...>
>>> plt.show()
The following pages refer to to this document either explicitly or contain code examples using this.
numpy.fft.fft
numpy.fft.rfftn
numpy.fft.ifftn
numpy.fft.rfft
numpy.fft.fft2
Hover to see nodes names; edges to Self not shown, Caped at 50 nodes.
Using a canvas is more power efficient and can get hundred of nodes ; but does not allow hyperlinks; , arrows or text (beyond on hover)
SVG is more flexible but power hungry; and does not scale well to 50 + nodes.
All aboves nodes referred to, (or are referred from) current nodes; Edges from Self to other have been omitted (or all nodes would be connected to the central node "self" which is not useful). Nodes are colored by the library they belong to, and scaled with the number of references pointing them