delaunay_plot_2d(tri, ax=None)
Requires Matplotlib.
Triangulation to plot
Axes to plot on
Figure for the plot
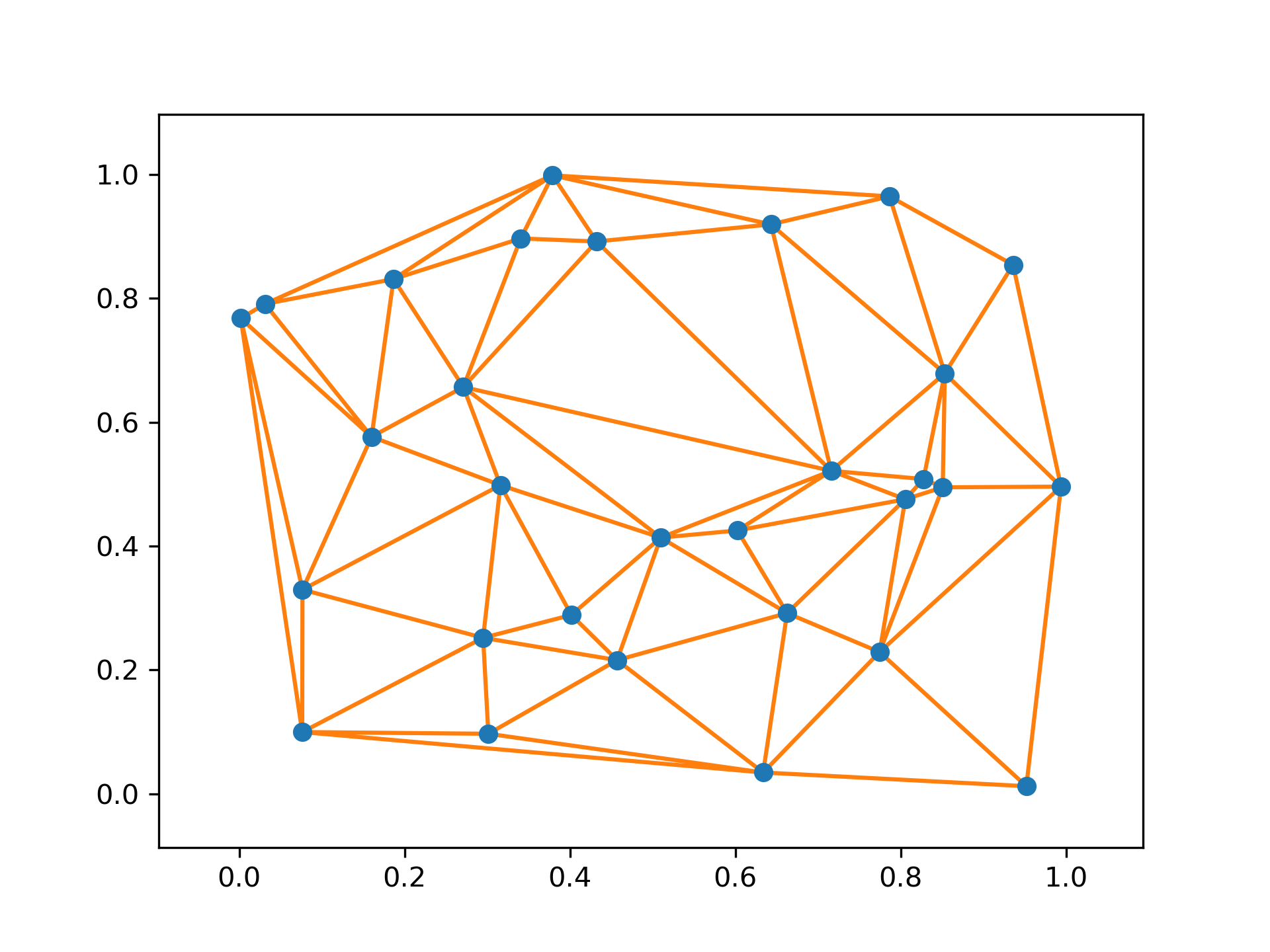
Plot the given Delaunay triangulation in 2-D
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
... from scipy.spatial import Delaunay, delaunay_plot_2d
The Delaunay triangulation of a set of random points:
>>> rng = np.random.default_rng()
... points = rng.random((30, 2))
... tri = Delaunay(points)
Plot it:
>>> _ = delaunay_plot_2d(tri)
... plt.show()
The following pages refer to to this document either explicitly or contain code examples using this.
scipy.spatial._qhull.tsearch
scipy.spatial._plotutils.delaunay_plot_2d
Hover to see nodes names; edges to Self not shown, Caped at 50 nodes.
Using a canvas is more power efficient and can get hundred of nodes ; but does not allow hyperlinks; , arrows or text (beyond on hover)
SVG is more flexible but power hungry; and does not scale well to 50 + nodes.
All aboves nodes referred to, (or are referred from) current nodes; Edges from Self to other have been omitted (or all nodes would be connected to the central node "self" which is not useful). Nodes are colored by the library they belong to, and scaled with the number of references pointing them