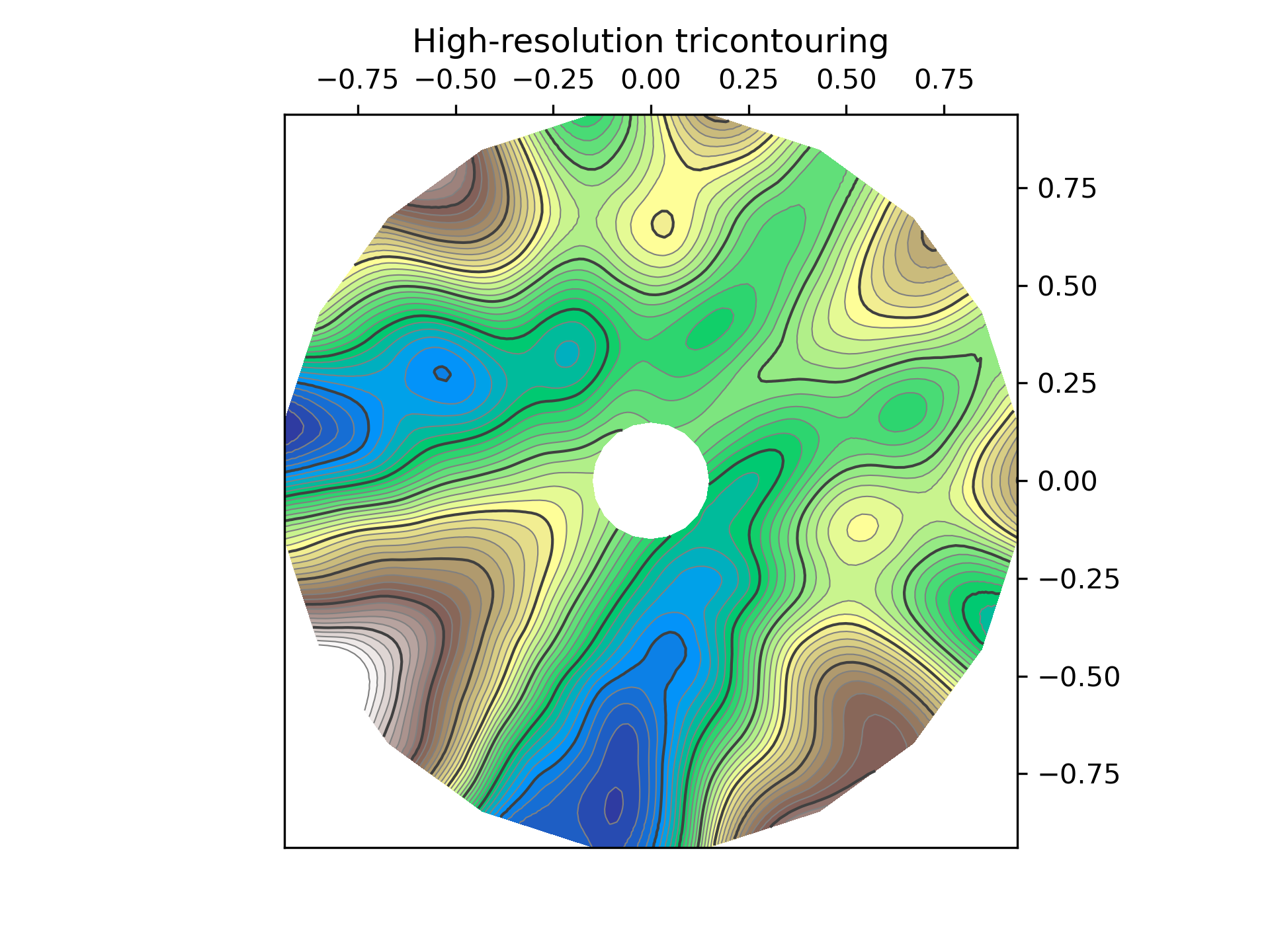
>>> """
======================
Tricontour Smooth User
======================
Demonstrates high-resolution tricontouring on user-defined triangular grids
with `matplotlib.tri.UniformTriRefiner`.
"""
... import matplotlib.tri as tri
... import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
... import numpy as np
...
...
... # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
... # Analytical test function
... # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
... def function_z(x, y):
... r1 = np.sqrt((0.5 - x)**2 + (0.5 - y)**2)
... theta1 = np.arctan2(0.5 - x, 0.5 - y)
... r2 = np.sqrt((-x - 0.2)**2 + (-y - 0.2)**2)
... theta2 = np.arctan2(-x - 0.2, -y - 0.2)
... z = -(2 * (np.exp((r1 / 10)**2) - 1) * 30. * np.cos(7. * theta1) +
... (np.exp((r2 / 10)**2) - 1) * 30. * np.cos(11. * theta2) +
... 0.7 * (x**2 + y**2))
... return (np.max(z) - z) / (np.max(z) - np.min(z))
...
... # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
... # Creating a Triangulation
... # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
... # First create the x and y coordinates of the points.
... n_angles = 20
... n_radii = 10
... min_radius = 0.15
... radii = np.linspace(min_radius, 0.95, n_radii)
...
... angles = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, n_angles, endpoint=False)
... angles = np.repeat(angles[..., np.newaxis], n_radii, axis=1)
... angles[:, 1::2] += np.pi / n_angles
...
... x = (radii * np.cos(angles)).flatten()
... y = (radii * np.sin(angles)).flatten()
... z = function_z(x, y)
...
... # Now create the Triangulation.
... # (Creating a Triangulation without specifying the triangles results in the
... # Delaunay triangulation of the points.)
... triang = tri.Triangulation(x, y)
...
... # Mask off unwanted triangles.
... triang.set_mask(np.hypot(x[triang.triangles].mean(axis=1),
... y[triang.triangles].mean(axis=1))
... < min_radius)
...
... # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
... # Refine data
... # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
... refiner = tri.UniformTriRefiner(triang)
... tri_refi, z_test_refi = refiner.refine_field(z, subdiv=3)
...
... # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
... # Plot the triangulation and the high-res iso-contours
... # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
... fig, ax = plt.subplots()
... ax.set_aspect('equal')
... ax.triplot(triang, lw=0.5, color='white')
...
... levels = np.arange(0., 1., 0.025)
... ax.tricontourf(tri_refi, z_test_refi, levels=levels, cmap='terrain')
... ax.tricontour(tri_refi, z_test_refi, levels=levels,
... colors=['0.25', '0.5', '0.5', '0.5', '0.5'],
... linewidths=[1.0, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5])
...
... ax.set_title("High-resolution tricontouring")
...
... plt.show()
...
... #############################################################################
... #
... # .. admonition:: References
... #
... # The use of the following functions, methods, classes and modules is shown
... # in this example:
... #
... # - `matplotlib.axes.Axes.tricontour` / `matplotlib.pyplot.tricontour`
... # - `matplotlib.axes.Axes.tricontourf` / `matplotlib.pyplot.tricontourf`
... # - `matplotlib.tri`
... # - `matplotlib.tri.Triangulation`
... # - `matplotlib.tri.UniformTriRefiner`
...