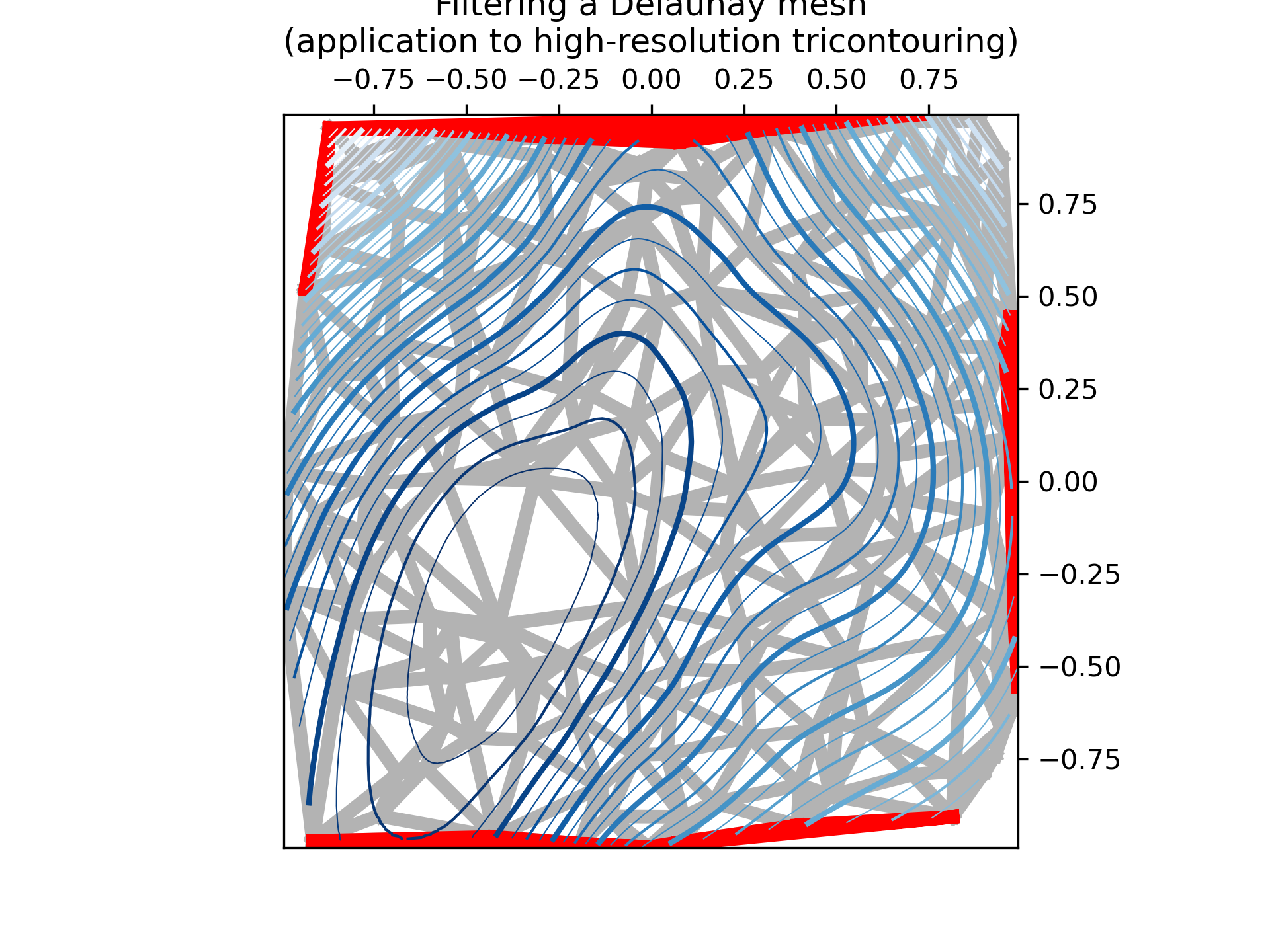
>>> """
==========================
Tricontour Smooth Delaunay
==========================
Demonstrates high-resolution tricontouring of a random set of points;
a `matplotlib.tri.TriAnalyzer` is used to improve the plot quality.
The initial data points and triangular grid for this demo are:
- a set of random points is instantiated, inside [-1, 1] x [-1, 1] square
- A Delaunay triangulation of these points is then computed, of which a
random subset of triangles is masked out by the user (based on
*init_mask_frac* parameter). This simulates invalidated data.
The proposed generic procedure to obtain a high resolution contouring of such
a data set is the following:
1. Compute an extended mask with a `matplotlib.tri.TriAnalyzer`, which will
exclude badly shaped (flat) triangles from the border of the
triangulation. Apply the mask to the triangulation (using set_mask).
2. Refine and interpolate the data using a `matplotlib.tri.UniformTriRefiner`.
3. Plot the refined data with `~.axes.Axes.tricontour`.
"""
... from matplotlib.tri import Triangulation, TriAnalyzer, UniformTriRefiner
... import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
... import numpy as np
...
...
... # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
... # Analytical test function
... # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
... def experiment_res(x, y):
... """An analytic function representing experiment results."""
... x = 2 * x
... r1 = np.sqrt((0.5 - x)**2 + (0.5 - y)**2)
... theta1 = np.arctan2(0.5 - x, 0.5 - y)
... r2 = np.sqrt((-x - 0.2)**2 + (-y - 0.2)**2)
... theta2 = np.arctan2(-x - 0.2, -y - 0.2)
... z = (4 * (np.exp((r1/10)**2) - 1) * 30 * np.cos(3 * theta1) +
... (np.exp((r2/10)**2) - 1) * 30 * np.cos(5 * theta2) +
... 2 * (x**2 + y**2))
... return (np.max(z) - z) / (np.max(z) - np.min(z))
...
... # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
... # Generating the initial data test points and triangulation for the demo
... # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
... # User parameters for data test points
...
... # Number of test data points, tested from 3 to 5000 for subdiv=3
... n_test = 200
...
... # Number of recursive subdivisions of the initial mesh for smooth plots.
... # Values >3 might result in a very high number of triangles for the refine
... # mesh: new triangles numbering = (4**subdiv)*ntri
... subdiv = 3
...
... # Float > 0. adjusting the proportion of (invalid) initial triangles which will
... # be masked out. Enter 0 for no mask.
... init_mask_frac = 0.0
...
... # Minimum circle ratio - border triangles with circle ratio below this will be
... # masked if they touch a border. Suggested value 0.01; use -1 to keep all
... # triangles.
... min_circle_ratio = .01
...
... # Random points
... random_gen = np.random.RandomState(seed=19680801)
... x_test = random_gen.uniform(-1., 1., size=n_test)
... y_test = random_gen.uniform(-1., 1., size=n_test)
... z_test = experiment_res(x_test, y_test)
...
... # meshing with Delaunay triangulation
... tri = Triangulation(x_test, y_test)
... ntri = tri.triangles.shape[0]
...
... # Some invalid data are masked out
... mask_init = np.zeros(ntri, dtype=bool)
... masked_tri = random_gen.randint(0, ntri, int(ntri * init_mask_frac))
... mask_init[masked_tri] = True
... tri.set_mask(mask_init)
...
...
... # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
... # Improving the triangulation before high-res plots: removing flat triangles
... # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
... # masking badly shaped triangles at the border of the triangular mesh.
... mask = TriAnalyzer(tri).get_flat_tri_mask(min_circle_ratio)
... tri.set_mask(mask)
...
... # refining the data
... refiner = UniformTriRefiner(tri)
... tri_refi, z_test_refi = refiner.refine_field(z_test, subdiv=subdiv)
...
... # analytical 'results' for comparison
... z_expected = experiment_res(tri_refi.x, tri_refi.y)
...
... # for the demo: loading the 'flat' triangles for plot
... flat_tri = Triangulation(x_test, y_test)
... flat_tri.set_mask(~mask)
...
...
... # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
... # Now the plots
... # ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
... # User options for plots
... plot_tri = True # plot of base triangulation
... plot_masked_tri = True # plot of excessively flat excluded triangles
... plot_refi_tri = False # plot of refined triangulation
... plot_expected = False # plot of analytical function values for comparison
...
...
... # Graphical options for tricontouring
... levels = np.arange(0., 1., 0.025)
...
... fig, ax = plt.subplots()
... ax.set_aspect('equal')
... ax.set_title("Filtering a Delaunay mesh\n"
... "(application to high-resolution tricontouring)")
...
... # 1) plot of the refined (computed) data contours:
... ax.tricontour(tri_refi, z_test_refi, levels=levels, cmap='Blues',
... linewidths=[2.0, 0.5, 1.0, 0.5])
... # 2) plot of the expected (analytical) data contours (dashed):
... if plot_expected:
... ax.tricontour(tri_refi, z_expected, levels=levels, cmap='Blues',
... linestyles='--')
... # 3) plot of the fine mesh on which interpolation was done:
... if plot_refi_tri:
... ax.triplot(tri_refi, color='0.97')
... # 4) plot of the initial 'coarse' mesh:
... if plot_tri:
... ax.triplot(tri, color='0.7')
... # 4) plot of the unvalidated triangles from naive Delaunay Triangulation:
... if plot_masked_tri:
... ax.triplot(flat_tri, color='red')
...
... plt.show()
...
... #############################################################################
... #
... # .. admonition:: References
... #
... # The use of the following functions, methods, classes and modules is shown
... # in this example:
... #
... # - `matplotlib.axes.Axes.tricontour` / `matplotlib.pyplot.tricontour`
... # - `matplotlib.axes.Axes.tricontourf` / `matplotlib.pyplot.tricontourf`
... # - `matplotlib.axes.Axes.triplot` / `matplotlib.pyplot.triplot`
... # - `matplotlib.tri`
... # - `matplotlib.tri.Triangulation`
... # - `matplotlib.tri.TriAnalyzer`
... # - `matplotlib.tri.UniformTriRefiner`
...