>>> """
========================
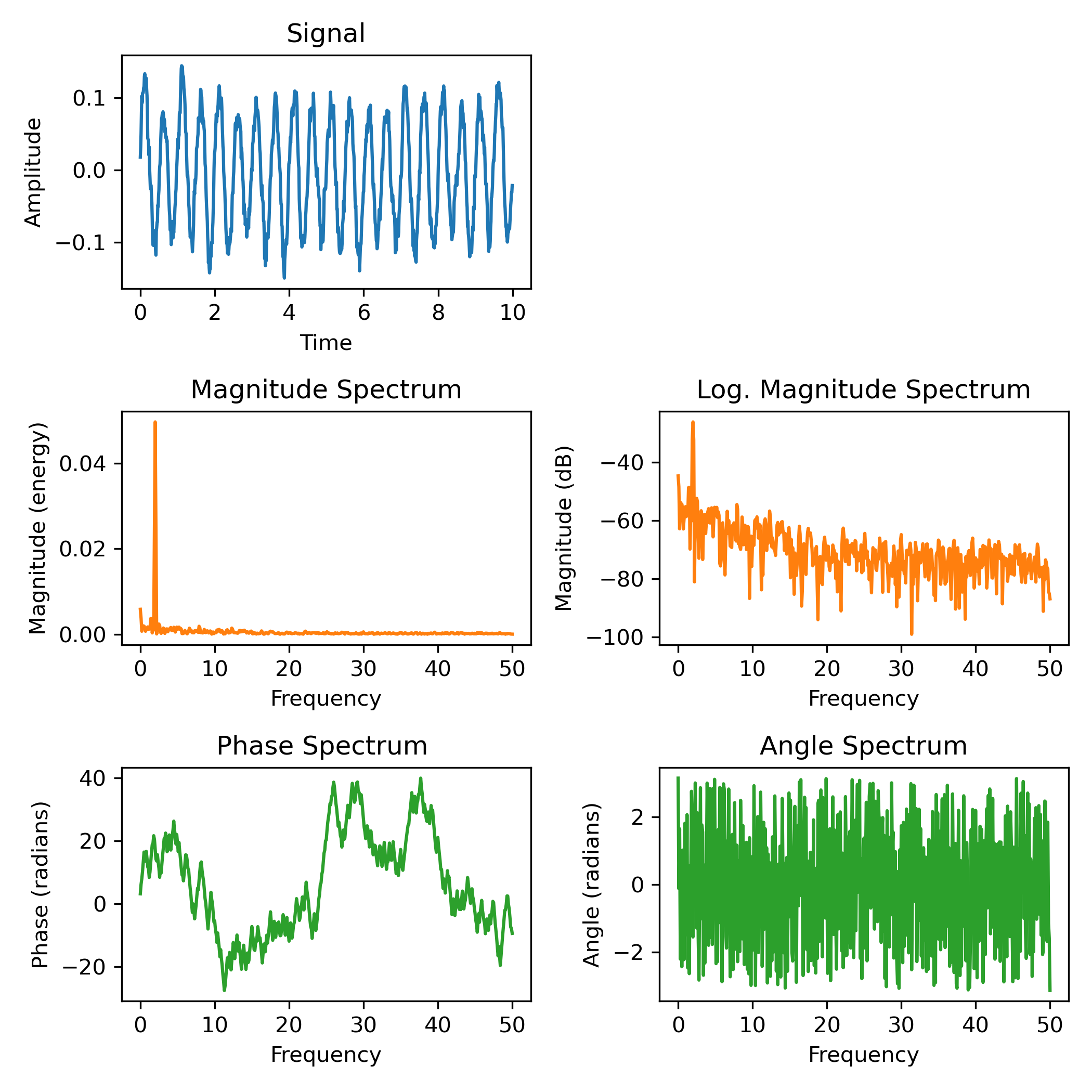
Spectrum Representations
========================
The plots show different spectrum representations of a sine signal with
additive noise. A (frequency) spectrum of a discrete-time signal is calculated
by utilizing the fast Fourier transform (FFT).
"""
... import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
... import numpy as np
...
...
... np.random.seed(0)
...
... dt = 0.01 # sampling interval
... Fs = 1 / dt # sampling frequency
... t = np.arange(0, 10, dt)
...
... # generate noise:
... nse = np.random.randn(len(t))
... r = np.exp(-t / 0.05)
... cnse = np.convolve(nse, r) * dt
... cnse = cnse[:len(t)]
...
... s = 0.1 * np.sin(4 * np.pi * t) + cnse # the signal
...
... fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=3, ncols=2, figsize=(7, 7))
...
... # plot time signal:
... axs[0, 0].set_title("Signal")
... axs[0, 0].plot(t, s, color='C0')
... axs[0, 0].set_xlabel("Time")
... axs[0, 0].set_ylabel("Amplitude")
...
... # plot different spectrum types:
... axs[1, 0].set_title("Magnitude Spectrum")
... axs[1, 0].magnitude_spectrum(s, Fs=Fs, color='C1')
...
... axs[1, 1].set_title("Log. Magnitude Spectrum")
... axs[1, 1].magnitude_spectrum(s, Fs=Fs, scale='dB', color='C1')
...
... axs[2, 0].set_title("Phase Spectrum ")
... axs[2, 0].phase_spectrum(s, Fs=Fs, color='C2')
...
... axs[2, 1].set_title("Angle Spectrum")
... axs[2, 1].angle_spectrum(s, Fs=Fs, color='C2')
...
... axs[0, 1].remove() # don't display empty ax
...
... fig.tight_layout()
... plt.show()
...