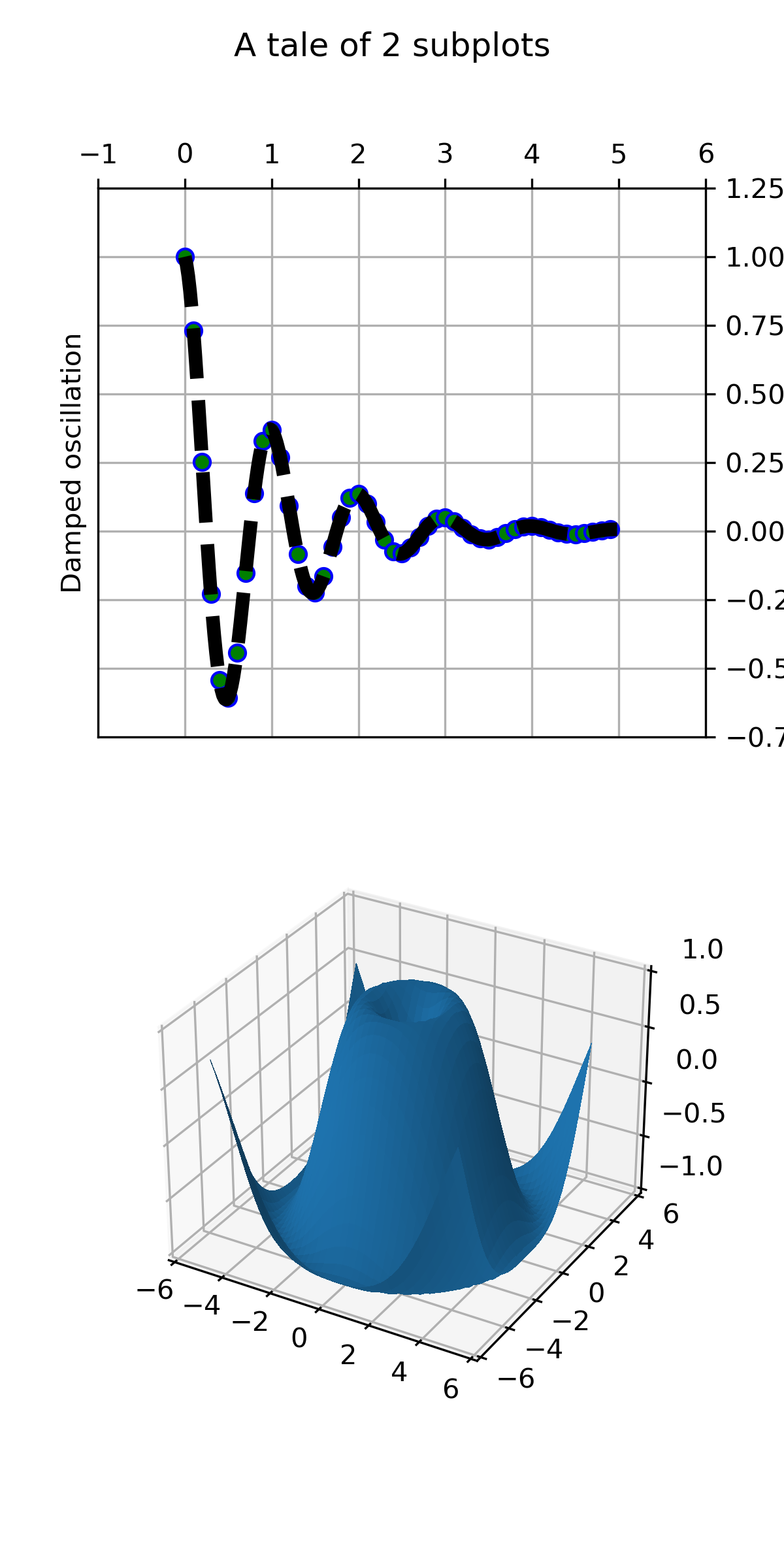
>>> """
=================================
2D and 3D *Axes* in same *Figure*
=================================
This example shows a how to plot a 2D and 3D plot on the same figure.
"""
...
... import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
... import numpy as np
...
...
... def f(t):
... return np.cos(2*np.pi*t) * np.exp(-t)
...
...
... # Set up a figure twice as tall as it is wide
... fig = plt.figure(figsize=plt.figaspect(2.))
... fig.suptitle('A tale of 2 subplots')
...
... # First subplot
... ax = fig.add_subplot(2, 1, 1)
...
... t1 = np.arange(0.0, 5.0, 0.1)
... t2 = np.arange(0.0, 5.0, 0.02)
... t3 = np.arange(0.0, 2.0, 0.01)
...
... ax.plot(t1, f(t1), 'bo',
... t2, f(t2), 'k--', markerfacecolor='green')
... ax.grid(True)
... ax.set_ylabel('Damped oscillation')
...
... # Second subplot
... ax = fig.add_subplot(2, 1, 2, projection='3d')
...
... X = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.25)
... Y = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.25)
... X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y)
... R = np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2)
... Z = np.sin(R)
...
... surf = ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1,
... linewidth=0, antialiased=False)
... ax.set_zlim(-1, 1)
...
... plt.show()
...