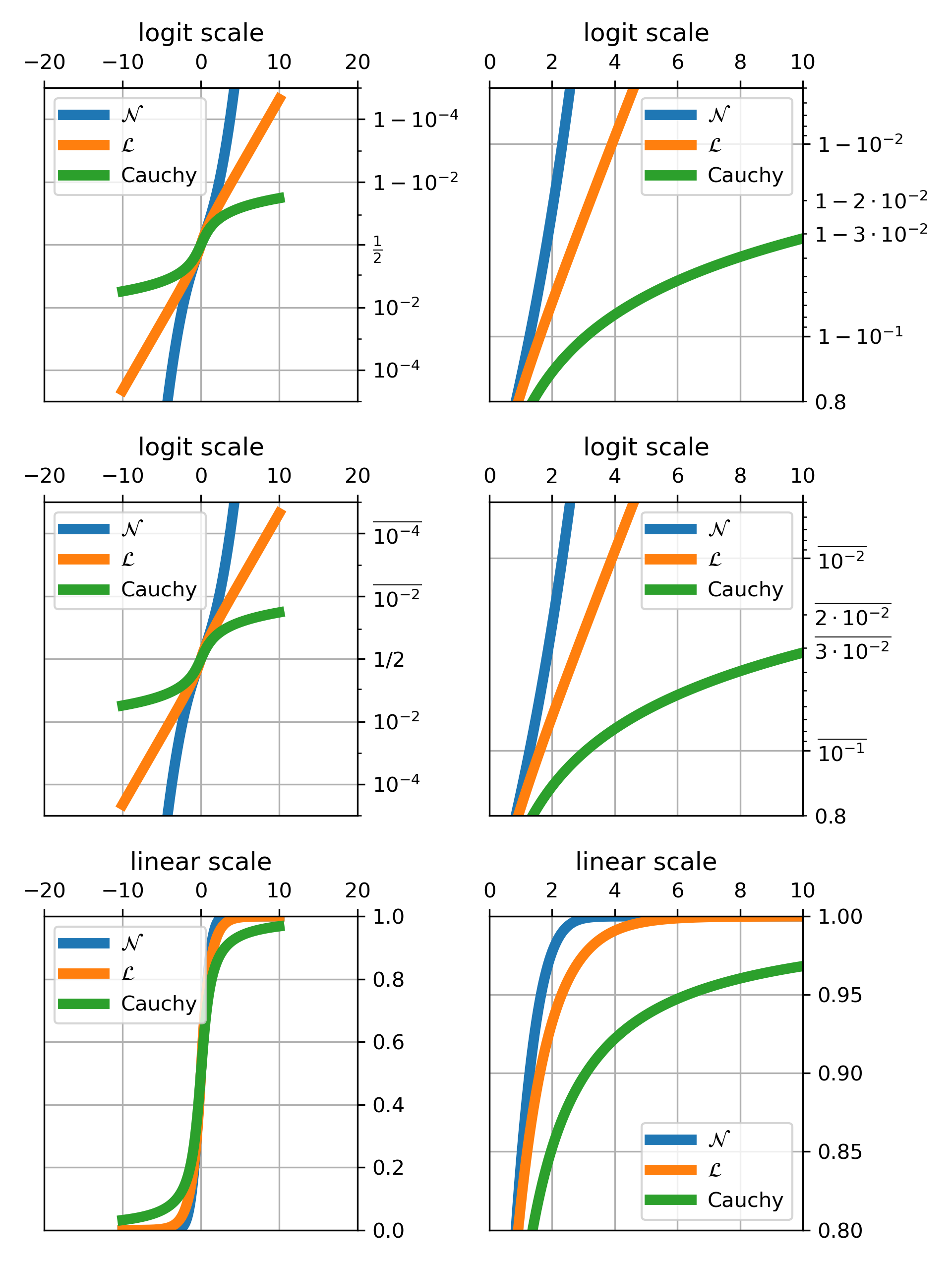
>>> """
================
Logit Demo
================
Examples of plots with logit axes.
"""
...
... import math
...
... import numpy as np
... import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
...
... xmax = 10
... x = np.linspace(-xmax, xmax, 10000)
... cdf_norm = [math.erf(w / np.sqrt(2)) / 2 + 1 / 2 for w in x]
... cdf_laplacian = np.where(x < 0, 1 / 2 * np.exp(x), 1 - 1 / 2 * np.exp(-x))
... cdf_cauchy = np.arctan(x) / np.pi + 1 / 2
...
... fig, axs = plt.subplots(nrows=3, ncols=2, figsize=(6.4, 8.5))
...
... # Common part, for the example, we will do the same plots on all graphs
... for i in range(3):
... for j in range(2):
... axs[i, j].plot(x, cdf_norm, label=r"$\mathcal{N}$")
... axs[i, j].plot(x, cdf_laplacian, label=r"$\mathcal{L}$")
... axs[i, j].plot(x, cdf_cauchy, label="Cauchy")
... axs[i, j].legend()
... axs[i, j].grid()
...
... # First line, logitscale, with standard notation
... axs[0, 0].set(title="logit scale")
... axs[0, 0].set_yscale("logit")
... axs[0, 0].set_ylim(1e-5, 1 - 1e-5)
...
... axs[0, 1].set(title="logit scale")
... axs[0, 1].set_yscale("logit")
... axs[0, 1].set_xlim(0, xmax)
... axs[0, 1].set_ylim(0.8, 1 - 5e-3)
...
... # Second line, logitscale, with survival notation (with `use_overline`), and
... # other format display 1/2
... axs[1, 0].set(title="logit scale")
... axs[1, 0].set_yscale("logit", one_half="1/2", use_overline=True)
... axs[1, 0].set_ylim(1e-5, 1 - 1e-5)
...
... axs[1, 1].set(title="logit scale")
... axs[1, 1].set_yscale("logit", one_half="1/2", use_overline=True)
... axs[1, 1].set_xlim(0, xmax)
... axs[1, 1].set_ylim(0.8, 1 - 5e-3)
...
... # Third line, linear scale
... axs[2, 0].set(title="linear scale")
... axs[2, 0].set_ylim(0, 1)
...
... axs[2, 1].set(title="linear scale")
... axs[2, 1].set_xlim(0, xmax)
... axs[2, 1].set_ylim(0.8, 1)
...
... fig.tight_layout()
... plt.show()
...