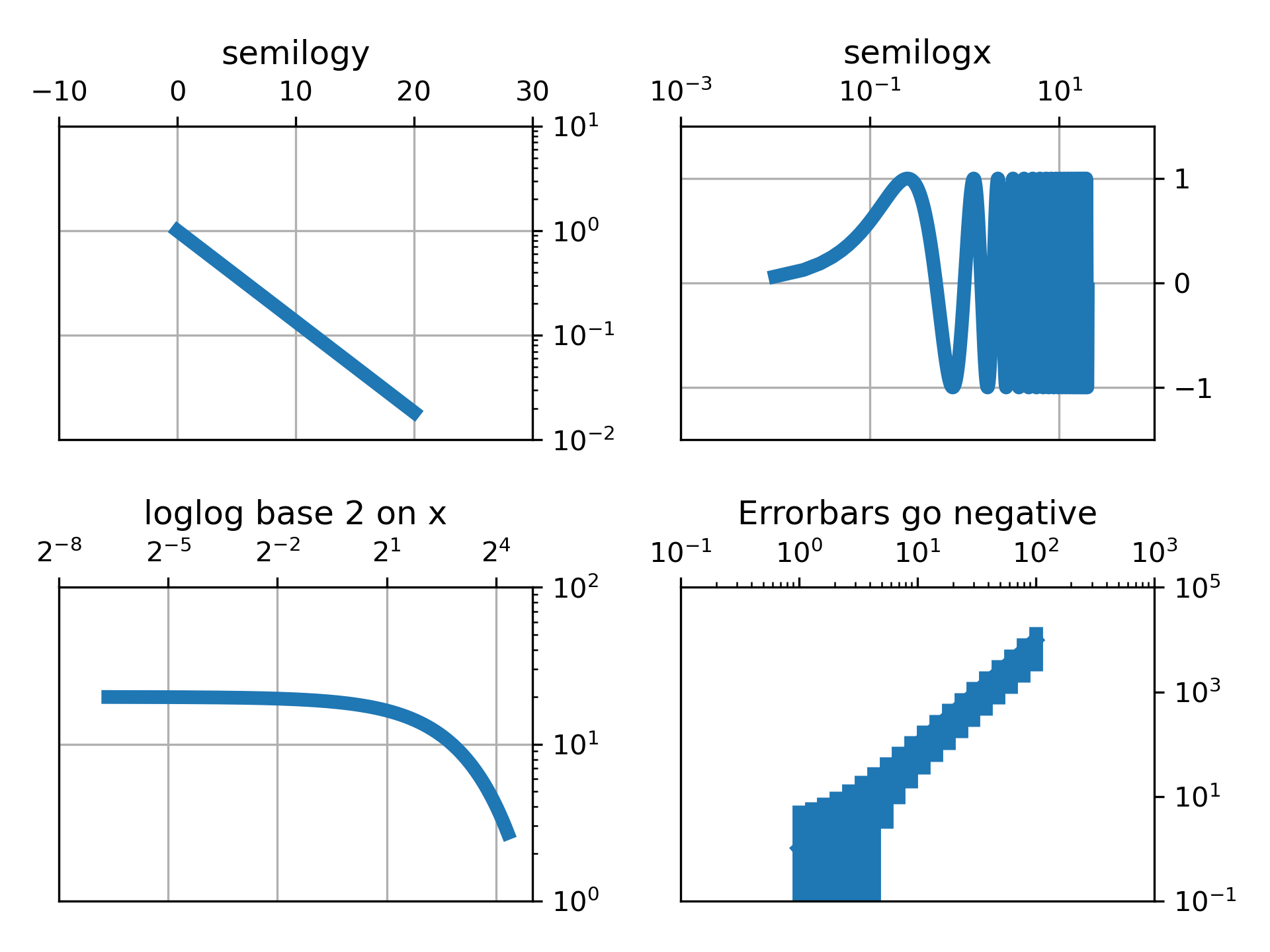
>>> """
========
Log Demo
========
Examples of plots with logarithmic axes.
"""
...
... import numpy as np
... import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
...
... # Data for plotting
... t = np.arange(0.01, 20.0, 0.01)
...
... # Create figure
... fig, ((ax1, ax2), (ax3, ax4)) = plt.subplots(2, 2)
...
... # log y axis
... ax1.semilogy(t, np.exp(-t / 5.0))
... ax1.set(title='semilogy')
... ax1.grid()
...
... # log x axis
... ax2.semilogx(t, np.sin(2 * np.pi * t))
... ax2.set(title='semilogx')
... ax2.grid()
...
... # log x and y axis
... ax3.loglog(t, 20 * np.exp(-t / 10.0))
... ax3.set_xscale('log', base=2)
... ax3.set(title='loglog base 2 on x')
... ax3.grid()
...
... # With errorbars: clip non-positive values
... # Use new data for plotting
... x = 10.0**np.linspace(0.0, 2.0, 20)
... y = x**2.0
...
... ax4.set_xscale("log", nonpositive='clip')
... ax4.set_yscale("log", nonpositive='clip')
... ax4.set(title='Errorbars go negative')
... ax4.errorbar(x, y, xerr=0.1 * x, yerr=5.0 + 0.75 * y)
... # ylim must be set after errorbar to allow errorbar to autoscale limits
... ax4.set_ylim(bottom=0.1)
...
... fig.tight_layout()
... plt.show()
...