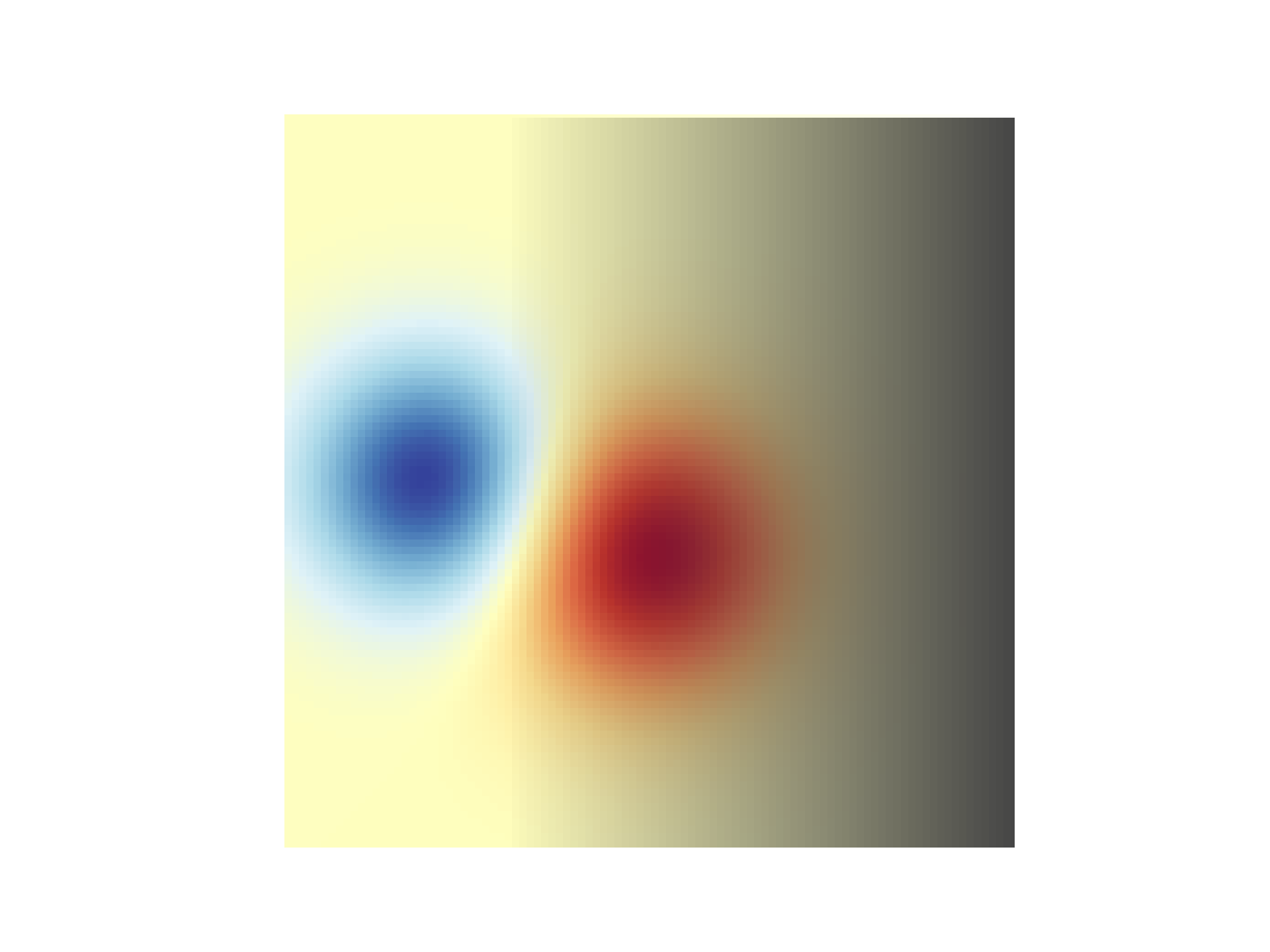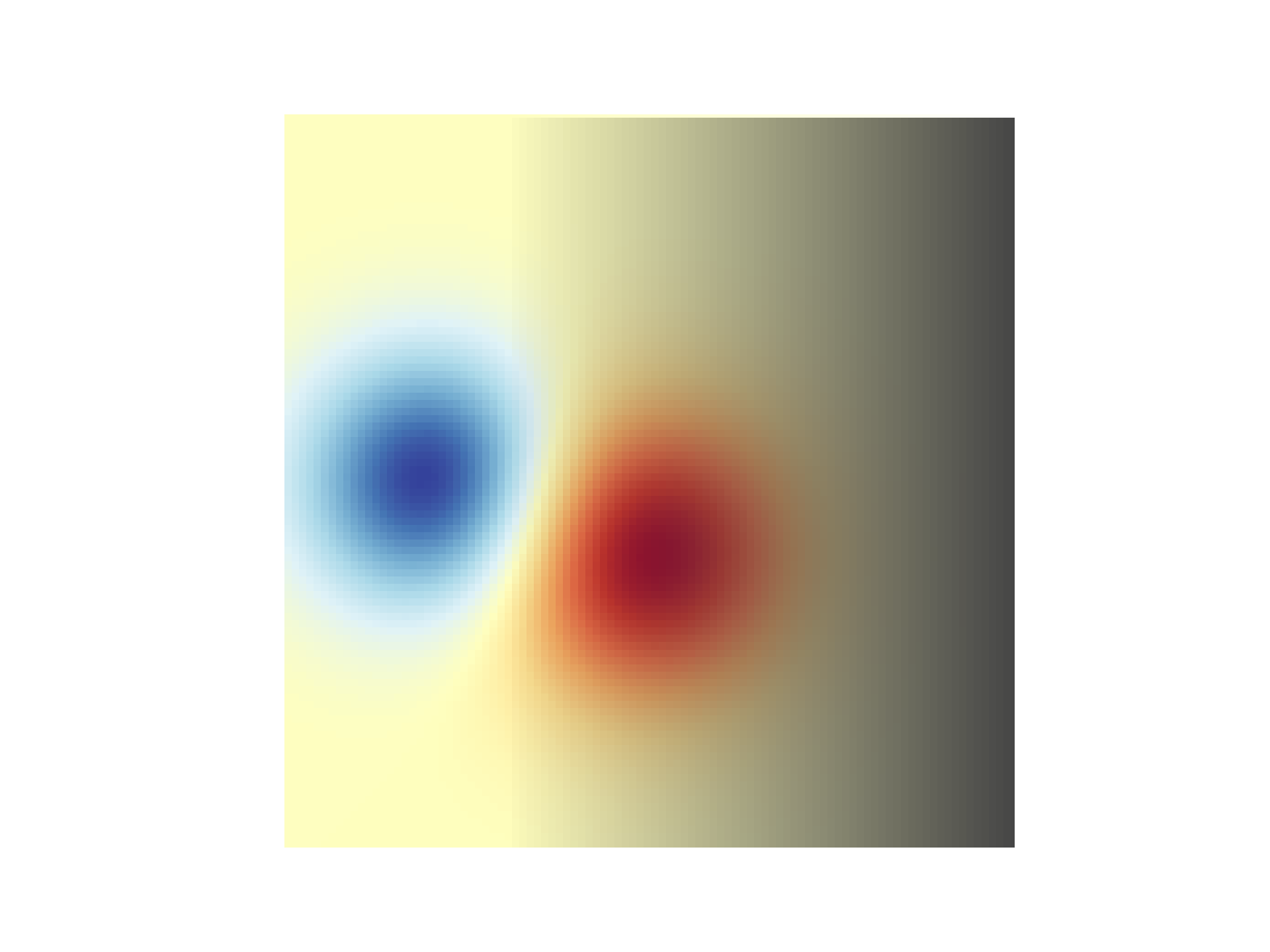>>> """
==========================================
Blend transparency with color in 2D images
==========================================
Blend transparency with color to highlight parts of data with imshow.
A common use for `matplotlib.pyplot.imshow` is to plot a 2D statistical
map. The function makes it easy to visualize a 2D matrix as an image and add
transparency to the output. For example, one can plot a statistic (such as a
t-statistic) and color the transparency of each pixel according to its p-value.
This example demonstrates how you can achieve this effect.
First we will generate some data, in this case, we'll create two 2D "blobs"
in a 2D grid. One blob will be positive, and the other negative.
"""
...
... # sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 3
... import numpy as np
... import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
... from matplotlib.colors import Normalize
...
...
... def normal_pdf(x, mean, var):
... return np.exp(-(x - mean)**2 / (2*var))
...
...
... # Generate the space in which the blobs will live
... xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax = (0, 100, 0, 100)
... n_bins = 100
... xx = np.linspace(xmin, xmax, n_bins)
... yy = np.linspace(ymin, ymax, n_bins)
...
... # Generate the blobs. The range of the values is roughly -.0002 to .0002
... means_high = [20, 50]
... means_low = [50, 60]
... var = [150, 200]
...
... gauss_x_high = normal_pdf(xx, means_high[0], var[0])
... gauss_y_high = normal_pdf(yy, means_high[1], var[0])
...
... gauss_x_low = normal_pdf(xx, means_low[0], var[1])
... gauss_y_low = normal_pdf(yy, means_low[1], var[1])
...
... weights = (np.outer(gauss_y_high, gauss_x_high)
... - np.outer(gauss_y_low, gauss_x_low))
...
... # We'll also create a grey background into which the pixels will fade
... greys = np.full((*weights.shape, 3), 70, dtype=np.uint8)
...
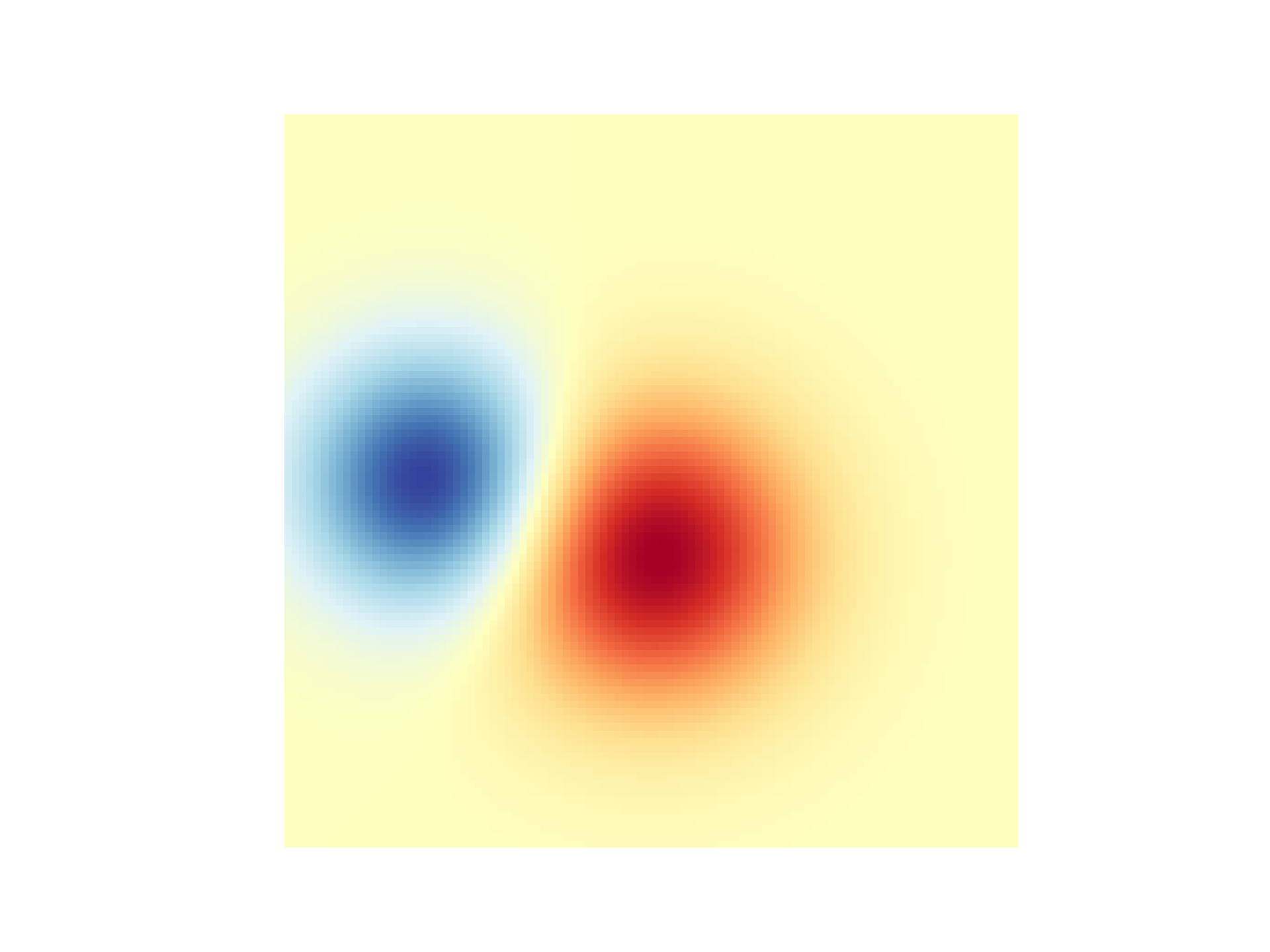
... # First we'll plot these blobs using ``imshow`` without transparency.
... vmax = np.abs(weights).max()
... imshow_kwargs = {
... 'vmax': vmax,
... 'vmin': -vmax,
... 'cmap': 'RdYlBu',
... 'extent': (xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax),
... }
...
... fig, ax = plt.subplots()
... ax.imshow(greys)
... ax.imshow(weights, **imshow_kwargs)
... ax.set_axis_off()
...
... ###############################################################################
... # Blending in transparency
... # ========================
... #
... # The simplest way to include transparency when plotting data with
... # `matplotlib.pyplot.imshow` is to pass an array matching the shape of
... # the data to the ``alpha`` argument. For example, we'll create a gradient
... # moving from left to right below.
...
... # Create an alpha channel of linearly increasing values moving to the right.
... alphas = np.ones(weights.shape)
... alphas[:, 30:] = np.linspace(1, 0, 70)
...
... # Create the figure and image
... # Note that the absolute values may be slightly different
... fig, ax = plt.subplots()
... ax.imshow(greys)
... ax.imshow(weights, alpha=alphas, **imshow_kwargs)
... ax.set_axis_off()
...
... ###############################################################################
... # Using transparency to highlight values with high amplitude
... # ==========================================================
... #
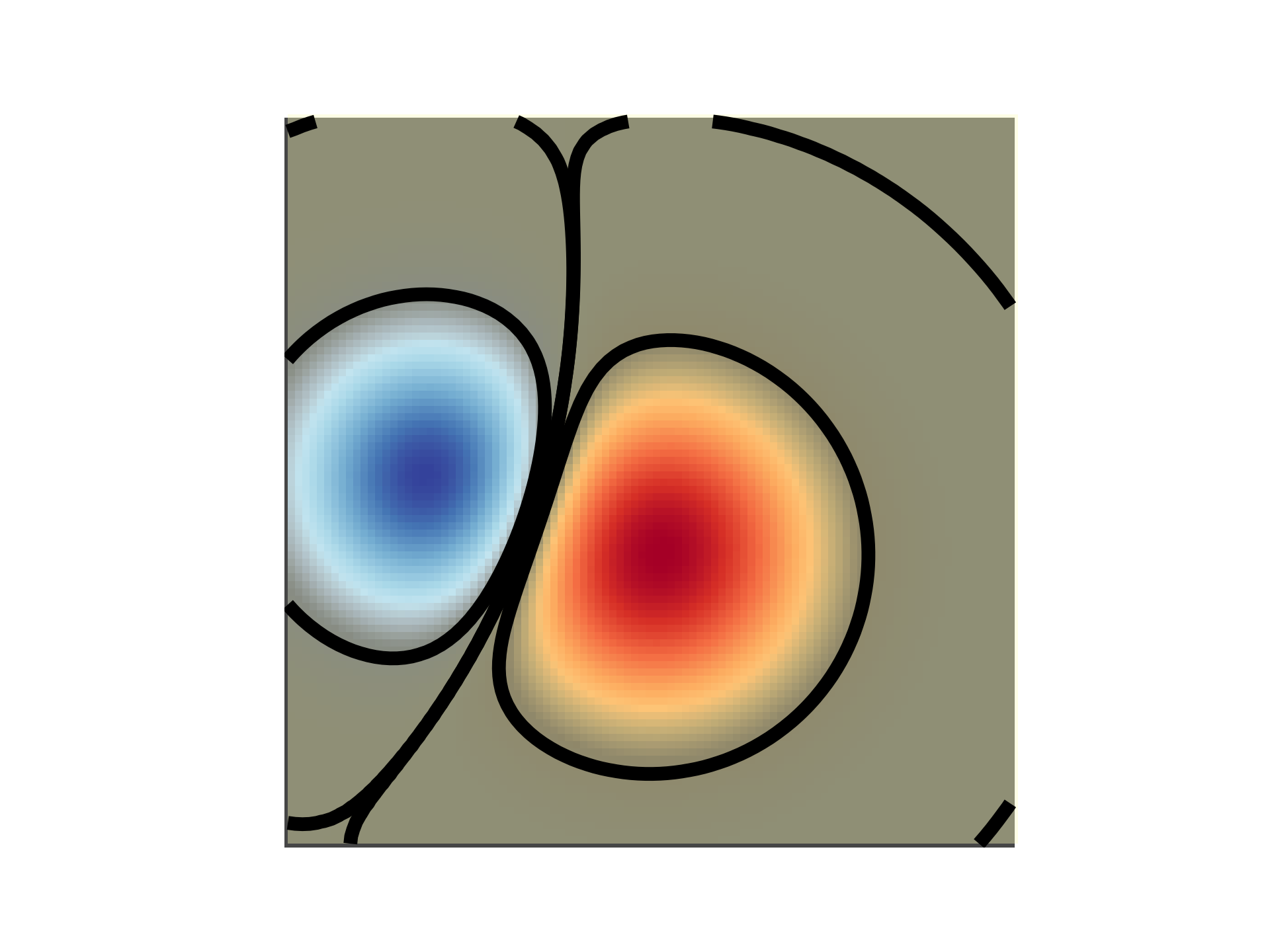
... # Finally, we'll recreate the same plot, but this time we'll use transparency
... # to highlight the extreme values in the data. This is often used to highlight
... # data points with smaller p-values. We'll also add in contour lines to
... # highlight the image values.
...
... # Create an alpha channel based on weight values
... # Any value whose absolute value is > .0001 will have zero transparency
... alphas = Normalize(0, .3, clip=True)(np.abs(weights))
... alphas = np.clip(alphas, .4, 1) # alpha value clipped at the bottom at .4
...
... # Create the figure and image
... # Note that the absolute values may be slightly different
... fig, ax = plt.subplots()
... ax.imshow(greys)
... ax.imshow(weights, alpha=alphas, **imshow_kwargs)
...
... # Add contour lines to further highlight different levels.
... ax.contour(weights[::-1], levels=[-.1, .1], colors='k', linestyles='-')
... ax.set_axis_off()
... plt.show()
...
... ax.contour(weights[::-1], levels=[-.0001, .0001], colors='k', linestyles='-')
... ax.set_axis_off()
... plt.show()
...
... #############################################################################
... #
... # .. admonition:: References
... #
... # The use of the following functions, methods, classes and modules is shown
... # in this example:
... #
... # - `matplotlib.axes.Axes.imshow` / `matplotlib.pyplot.imshow`
... # - `matplotlib.axes.Axes.contour` / `matplotlib.pyplot.contour`
... # - `matplotlib.colors.Normalize`
... # - `matplotlib.axes.Axes.set_axis_off`
...