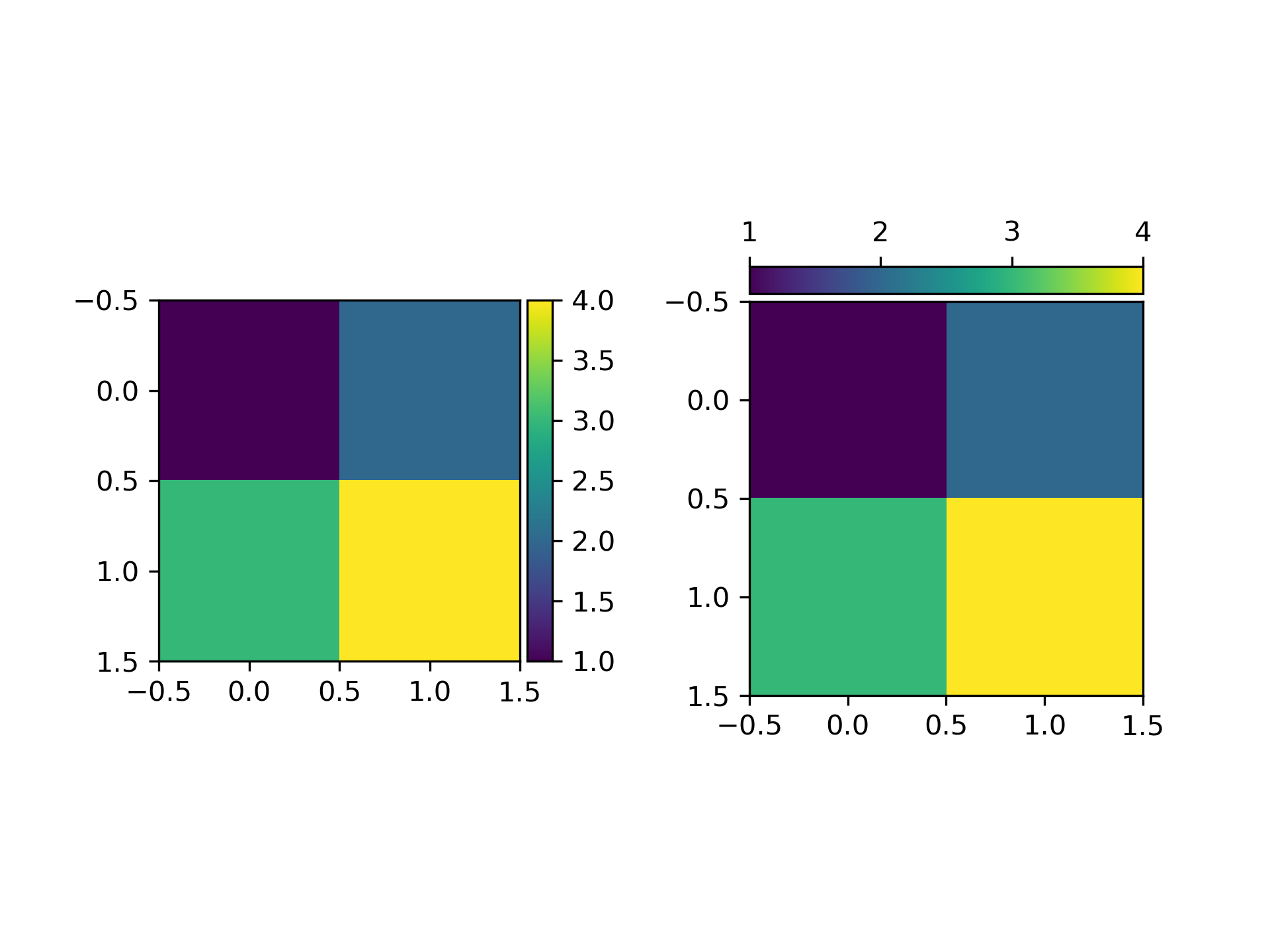
>>> """
============================
Colorbar with `.AxesDivider`
============================
The `.axes_divider.make_axes_locatable` function takes an existing axes, adds
it to a new `.AxesDivider` and returns the `.AxesDivider`. The `.append_axes`
method of the `.AxesDivider` can then be used to create a new axes on a given
side ("top", "right", "bottom", or "left") of the original axes. This example
uses `.append_axes` to add colorbars next to axes.
"""
...
... import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
... from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1.axes_divider import make_axes_locatable
...
... fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2)
... fig.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.5)
...
... im1 = ax1.imshow([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
... ax1_divider = make_axes_locatable(ax1)
... # Add an axes to the right of the main axes.
... cax1 = ax1_divider.append_axes("right", size="7%", pad="2%")
... cb1 = fig.colorbar(im1, cax=cax1)
...
... im2 = ax2.imshow([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
... ax2_divider = make_axes_locatable(ax2)
... # Add an axes above the main axes.
... cax2 = ax2_divider.append_axes("top", size="7%", pad="2%")
... cb2 = fig.colorbar(im2, cax=cax2, orientation="horizontal")
... # Change tick position to top (with the default tick position "bottom", ticks
... # overlap the image).
... cax2.xaxis.set_ticks_position("top")
...
... plt.show()
...