>>> r"""
=================
Custom box styles
=================
This example demonstrates the implementation of a custom `.BoxStyle`.
Custom `.ConnectionStyle`\s and `.ArrowStyle`\s can be similarly defined.
"""
...
... from matplotlib.patches import BoxStyle
... from matplotlib.path import Path
... import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
...
...
... ###############################################################################
... # Custom box styles can be implemented as a function that takes arguments
... # specifying both a rectangular box and the amount of "mutation", and
... # returns the "mutated" path. The specific signature is the one of
... # ``custom_box_style`` below.
... #
... # Here, we return a new path which adds an "arrow" shape on the left of the
... # box.
... #
... # The custom box style can then be used by passing
... # ``bbox=dict(boxstyle=custom_box_style, ...)`` to `.Axes.text`.
...
...
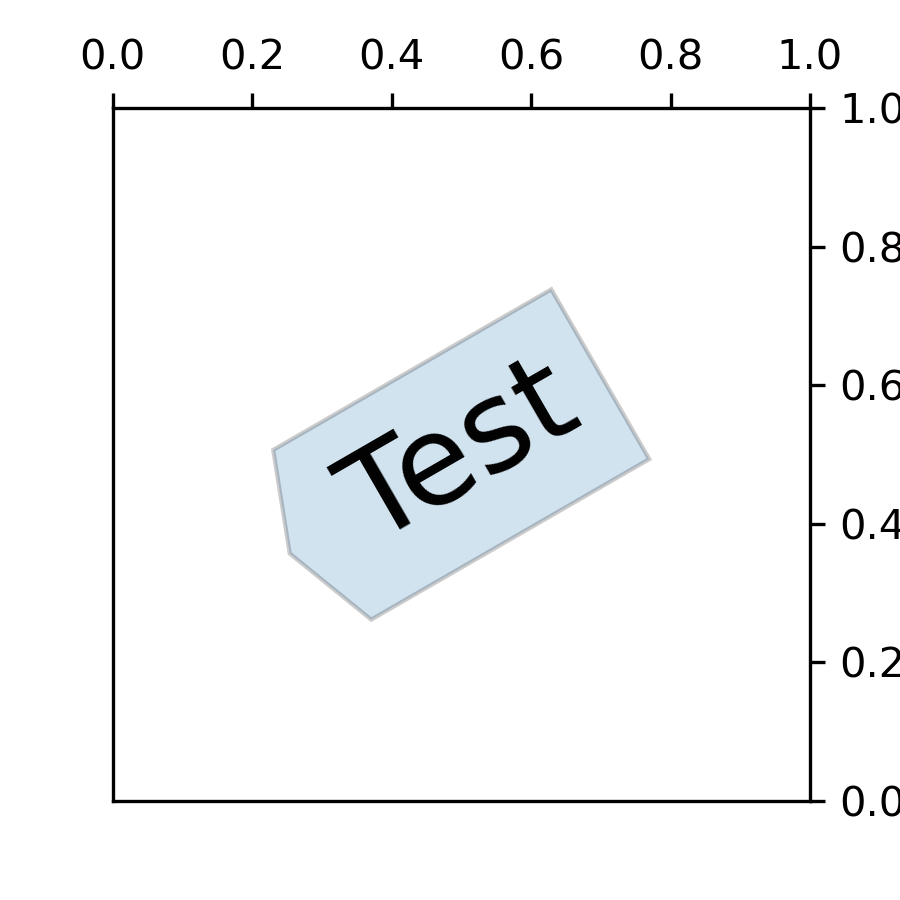
... def custom_box_style(x0, y0, width, height, mutation_size):
... """
Given the location and size of the box, return the path of the box around
it.
Rotation is automatically taken care of.
Parameters
----------
x0, y0, width, height : float
Box location and size.
mutation_size : float
Mutation reference scale, typically the text font size.
"""
... # padding
... mypad = 0.3
... pad = mutation_size * mypad
... # width and height with padding added.
... width = width + 2 * pad
... height = height + 2 * pad
... # boundary of the padded box
... x0, y0 = x0 - pad, y0 - pad
... x1, y1 = x0 + width, y0 + height
... # return the new path
... return Path([(x0, y0),
... (x1, y0), (x1, y1), (x0, y1),
... (x0-pad, (y0+y1)/2), (x0, y0),
... (x0, y0)],
... closed=True)
...
...
... fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(3, 3))
... ax.text(0.5, 0.5, "Test", size=30, va="center", ha="center", rotation=30,
... bbox=dict(boxstyle=custom_box_style, alpha=0.2))
...
...
... ###############################################################################
... # Likewise, custom box styles can be implemented as classes that implement
... # ``__call__``.
... #
... # The classes can then be registered into the ``BoxStyle._style_list`` dict,
... # which allows specifying the box style as a string,
... # ``bbox=dict(boxstyle="registered_name,param=value,...", ...)``.
... # Note that this registration relies on internal APIs and is therefore not
... # officially supported.
...
...
... class MyStyle:
... """A simple box."""
...
... def __init__(self, pad=0.3):
... """
The arguments must be floats and have default values.
Parameters
----------
pad : float
amount of padding
"""
... self.pad = pad
... super().__init__()
...
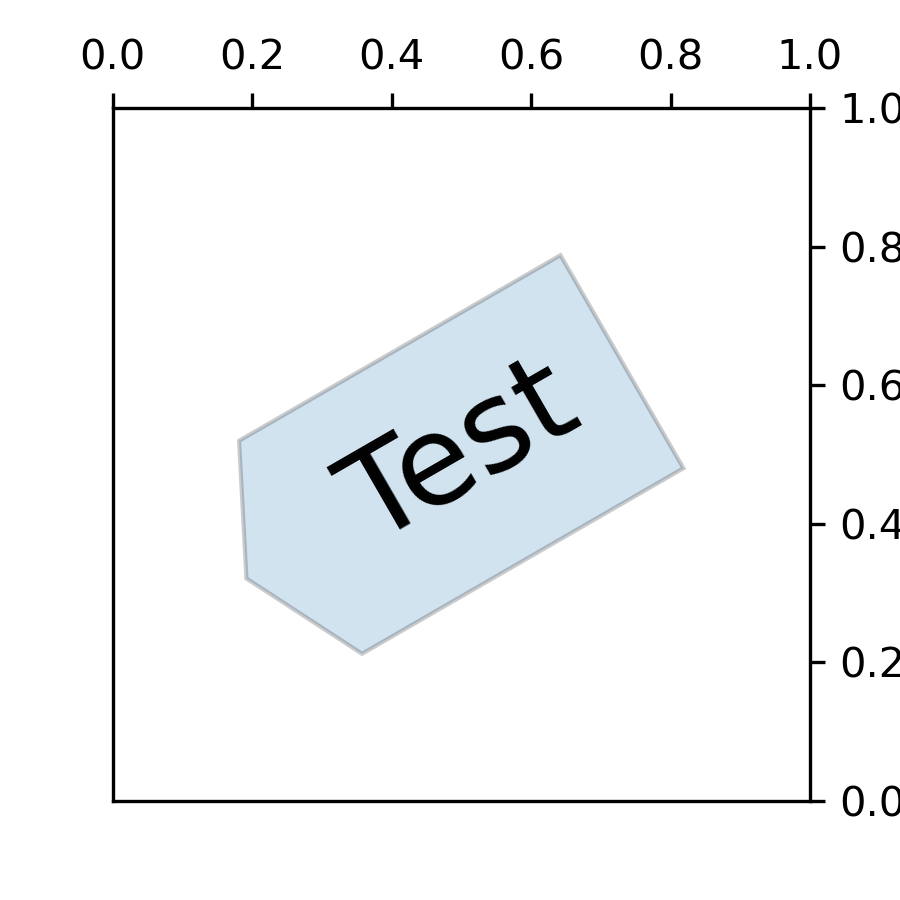
... def __call__(self, x0, y0, width, height, mutation_size):
... """
Given the location and size of the box, return the path of the box
around it.
Rotation is automatically taken care of.
Parameters
----------
x0, y0, width, height : float
Box location and size.
mutation_size : float
Reference scale for the mutation, typically the text font size.
"""
... # padding
... pad = mutation_size * self.pad
... # width and height with padding added
... width = width + 2.*pad
... height = height + 2.*pad
... # boundary of the padded box
... x0, y0 = x0 - pad, y0 - pad
... x1, y1 = x0 + width, y0 + height
... # return the new path
... return Path([(x0, y0),
... (x1, y0), (x1, y1), (x0, y1),
... (x0-pad, (y0+y1)/2.), (x0, y0),
... (x0, y0)],
... closed=True)
...
...
... BoxStyle._style_list["angled"] = MyStyle # Register the custom style.
...
... fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(3, 3))
... ax.text(0.5, 0.5, "Test", size=30, va="center", ha="center", rotation=30,
... bbox=dict(boxstyle="angled,pad=0.5", alpha=0.2))
...
... del BoxStyle._style_list["angled"] # Unregister it.
...
... plt.show()
...