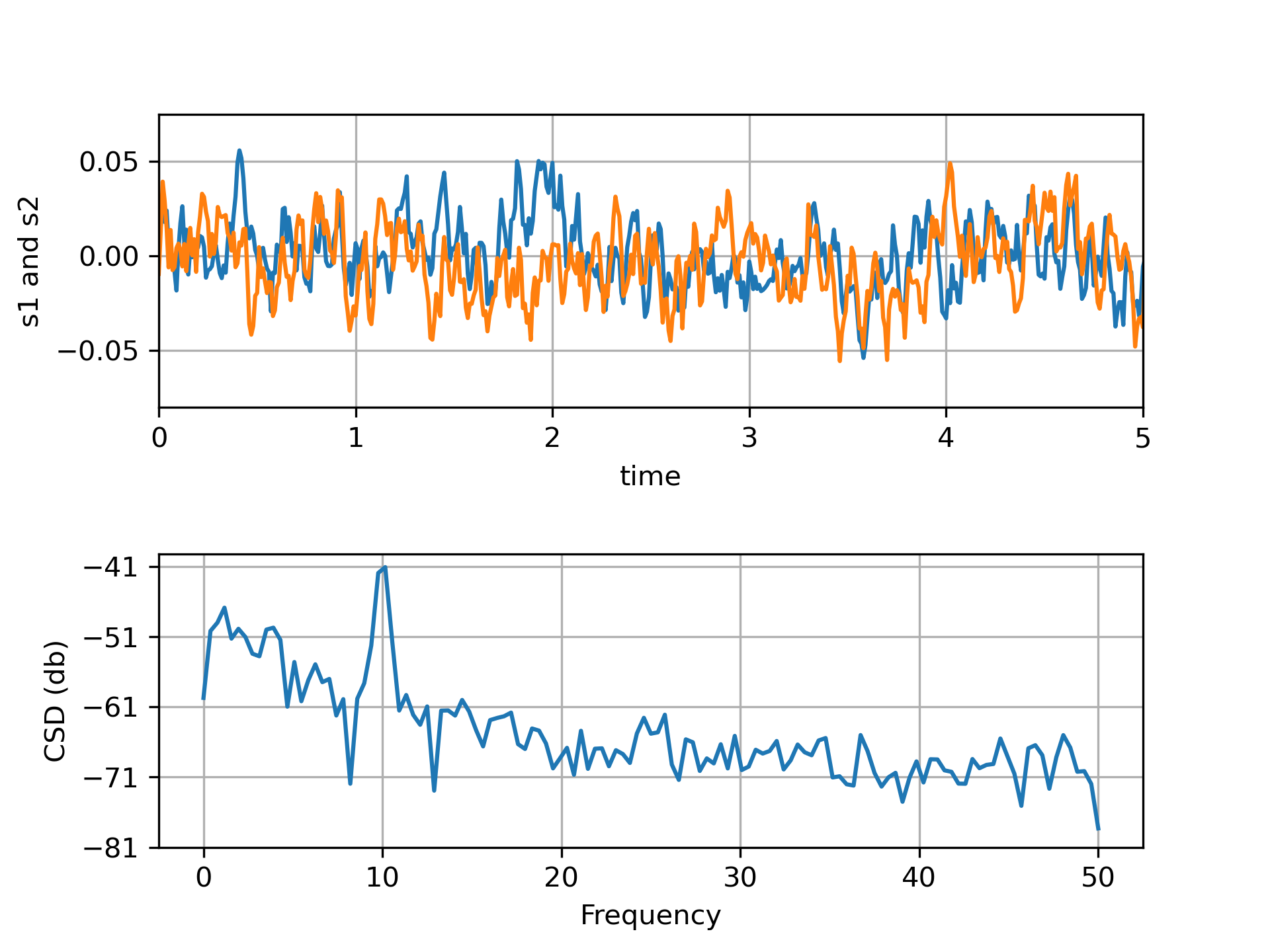
>>> """
========
CSD Demo
========
Compute the cross spectral density of two signals
"""
... import numpy as np
... import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
...
...
... fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(2, 1)
... # make a little extra space between the subplots
... fig.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.5)
...
... dt = 0.01
... t = np.arange(0, 30, dt)
...
... # Fixing random state for reproducibility
... np.random.seed(19680801)
...
...
... nse1 = np.random.randn(len(t)) # white noise 1
... nse2 = np.random.randn(len(t)) # white noise 2
... r = np.exp(-t / 0.05)
...
... cnse1 = np.convolve(nse1, r, mode='same') * dt # colored noise 1
... cnse2 = np.convolve(nse2, r, mode='same') * dt # colored noise 2
...
... # two signals with a coherent part and a random part
... s1 = 0.01 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * 10 * t) + cnse1
... s2 = 0.01 * np.sin(2 * np.pi * 10 * t) + cnse2
...
... ax1.plot(t, s1, t, s2)
... ax1.set_xlim(0, 5)
... ax1.set_xlabel('time')
... ax1.set_ylabel('s1 and s2')
... ax1.grid(True)
...
... cxy, f = ax2.csd(s1, s2, 256, 1. / dt)
... ax2.set_ylabel('CSD (db)')
... plt.show()
...