>>> """
======================================================
Controlling view limits using margins and sticky_edges
======================================================
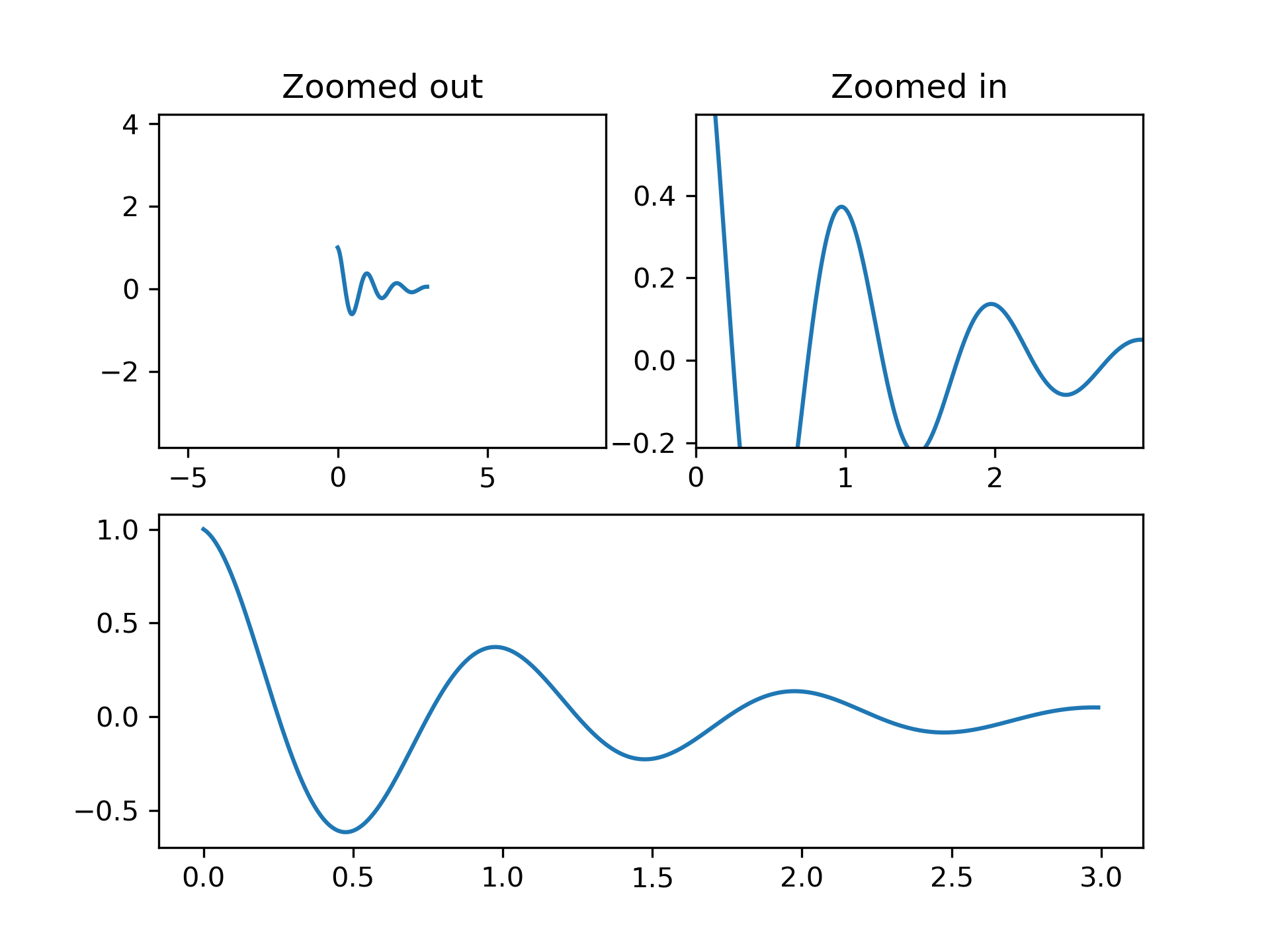
The first figure in this example shows how to zoom in and out of a
plot using `~.Axes.margins` instead of `~.Axes.set_xlim` and
`~.Axes.set_ylim`. The second figure demonstrates the concept of
edge "stickiness" introduced by certain methods and artists and how
to effectively work around that.
"""
...
... import numpy as np
... import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
... from matplotlib.patches import Polygon
...
...
... def f(t):
... return np.exp(-t) * np.cos(2*np.pi*t)
...
...
... t1 = np.arange(0.0, 3.0, 0.01)
...
... ax1 = plt.subplot(212)
... ax1.margins(0.05) # Default margin is 0.05, value 0 means fit
... ax1.plot(t1, f(t1))
...
... ax2 = plt.subplot(221)
... ax2.margins(2, 2) # Values >0.0 zoom out
... ax2.plot(t1, f(t1))
... ax2.set_title('Zoomed out')
...
... ax3 = plt.subplot(222)
... ax3.margins(x=0, y=-0.25) # Values in (-0.5, 0.0) zooms in to center
... ax3.plot(t1, f(t1))
... ax3.set_title('Zoomed in')
...
... plt.show()
...
...
... #############################################################################
... #
... # On the "stickiness" of certain plotting methods
... # """""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""""
... #
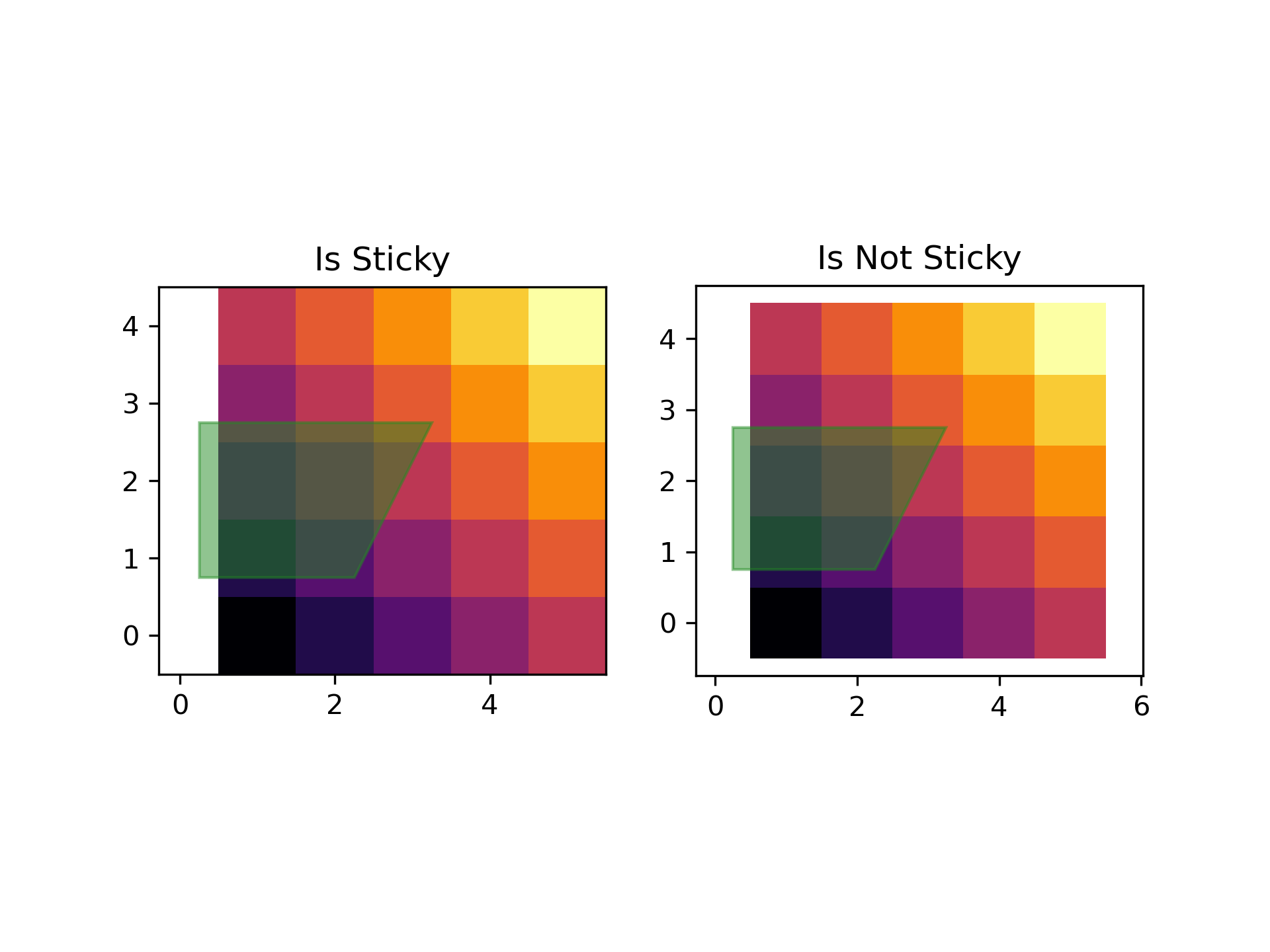
... # Some plotting functions make the axis limits "sticky" or immune to the will
... # of the `~.Axes.margins` methods. For instance, `~.Axes.imshow` and
... # `~.Axes.pcolor` expect the user to want the limits to be tight around the
... # pixels shown in the plot. If this behavior is not desired, you need to set
... # `~.Axes.use_sticky_edges` to `False`. Consider the following example:
...
... y, x = np.mgrid[:5, 1:6]
... poly_coords = [
... (0.25, 2.75), (3.25, 2.75),
... (2.25, 0.75), (0.25, 0.75)
... ]
... fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(ncols=2)
...
... # Here we set the stickiness of the axes object...
... # ax1 we'll leave as the default, which uses sticky edges
... # and we'll turn off stickiness for ax2
... ax2.use_sticky_edges = False
...
... for ax, status in zip((ax1, ax2), ('Is', 'Is Not')):
... cells = ax.pcolor(x, y, x+y, cmap='inferno', shading='auto') # sticky
... ax.add_patch(
... Polygon(poly_coords, color='forestgreen', alpha=0.5)
... ) # not sticky
... ax.margins(x=0.1, y=0.05)
... ax.set_aspect('equal')
... ax.set_title('{} Sticky'.format(status))
...
... plt.show()
...
...
... #############################################################################
... #
... # .. admonition:: References
... #
... # The use of the following functions, methods, classes and modules is shown
... # in this example:
... #
... # - `matplotlib.axes.Axes.margins` / `matplotlib.pyplot.margins`
... # - `matplotlib.axes.Axes.use_sticky_edges`
... # - `matplotlib.axes.Axes.pcolor` / `matplotlib.pyplot.pcolor`
... # - `matplotlib.patches.Polygon`
...