>>> """
==================
Annotate Transform
==================
This example shows how to use different coordinate systems for annotations.
For a complete overview of the annotation capabilities, also see the
:doc:`annotation tutorial</tutorials/text/annotations>`.
"""
...
... import numpy as np
... import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
...
... x = np.arange(0, 10, 0.005)
... y = np.exp(-x/2.) * np.sin(2*np.pi*x)
...
... fig, ax = plt.subplots()
... ax.plot(x, y)
... ax.set_xlim(0, 10)
... ax.set_ylim(-1, 1)
...
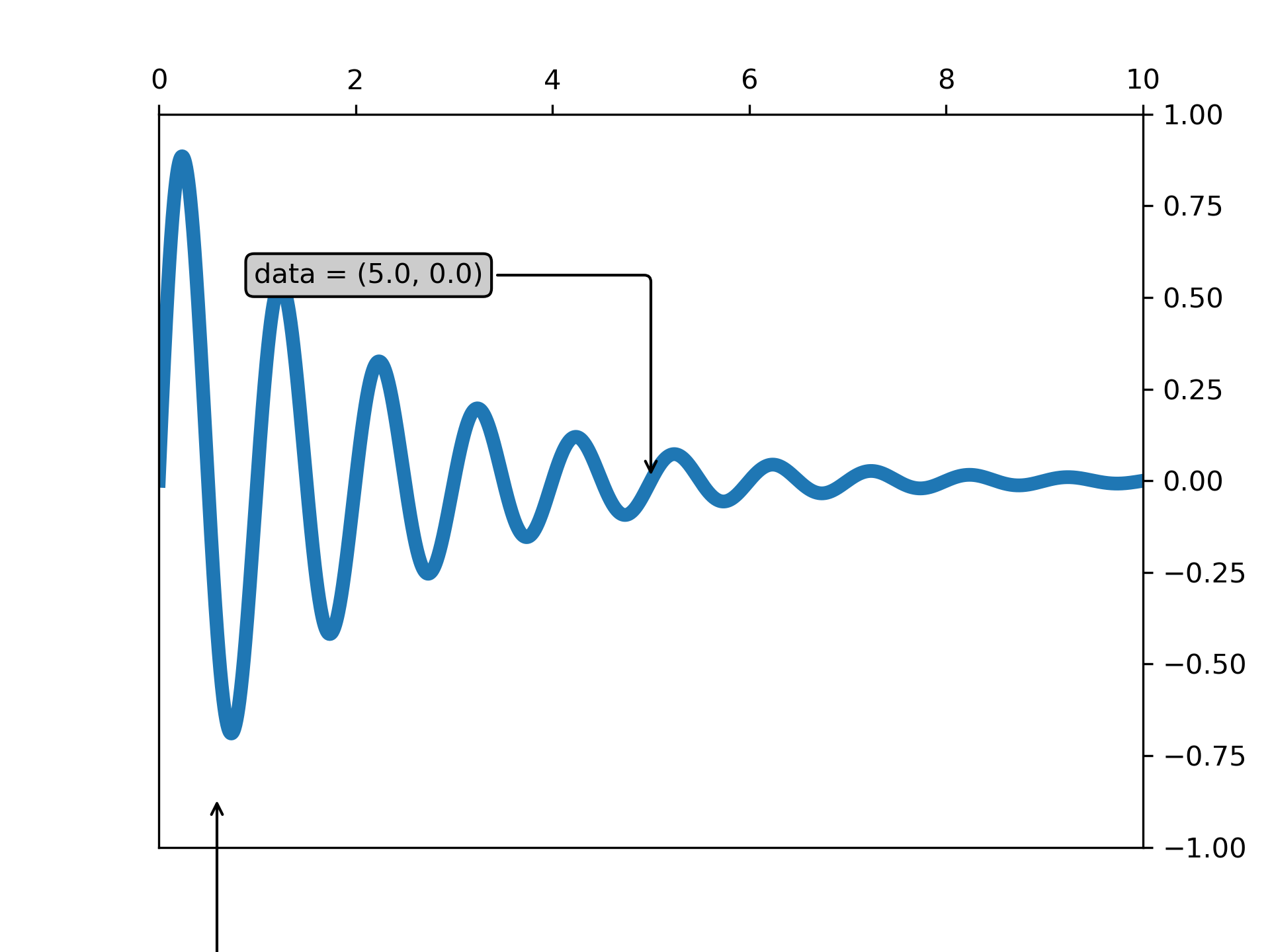
... xdata, ydata = 5, 0
... xdisplay, ydisplay = ax.transData.transform((xdata, ydata))
...
... bbox = dict(boxstyle="round", fc="0.8")
... arrowprops = dict(
... arrowstyle="->",
... connectionstyle="angle,angleA=0,angleB=90,rad=10")
...
... offset = 72
... ax.annotate(
... f'data = ({xdata:.1f}, {ydata:.1f})',
... (xdata, ydata),
... xytext=(-2*offset, offset), textcoords='offset points',
... bbox=bbox, arrowprops=arrowprops)
... ax.annotate(
... f'display = ({xdisplay:.1f}, {ydisplay:.1f})',
... xy=(xdisplay, ydisplay), xycoords='figure pixels',
... xytext=(0.5*offset, -offset), textcoords='offset points',
... bbox=bbox, arrowprops=arrowprops)
...
... plt.show()
...
... #############################################################################
... #
... # .. admonition:: References
... #
... # The use of the following functions, methods, classes and modules is shown
... # in this example:
... #
... # - `matplotlib.transforms.Transform.transform`
... # - `matplotlib.axes.Axes.annotate` / `matplotlib.pyplot.annotate`
...